cout
usage : cout << output value or variable << output value or variable .. ;
- "<<" is also known as "put to."
- o(out)stream 클래스로 만들어진 객체 < iostream
- 순서대로 출력
- 자동으로 변수나 상수의 자료형 검사 후 출력
cin
usage : cin >> input value or variable >> input value or variable ...;
- ">>" is also known as "get from."
- i(in)stream 클래스로 만들어진 객체 < iostream
- 순서대로 입력받고 자동으로 변수의 자료형 검사 후 저장
- 하나 이상의 변수를 반는 경우 space, enter로 구분 ( python split 과 비슷한 기능으로 예상 )
// iostream_cin.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
cout << "enter choice:";
cin >> x;
while (x < 1 || x > 4)
{
cout << "Invalid choice, try again:";
cin >> x;
// not a numeric character, probably
// clear the failure and pull off the non-numeric character
if (cin.fail())
{
cin.clear();
char c;
cin >> c;
cout << "c is " << c << endl;
}
}
cout << "your choice number : " << x << endl;
}
// 출처 : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/standard-library/iostream?view=msvc-170#cin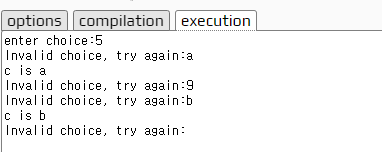
get
usage : cin.get(argument 1, argument 2)
- 문자열 입력
- argument 1 : address
- argument 2 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char line[25];
cout << " Type a line terminated by carriage return\n>";
cin.get( line, 25 );
cout << line << endl;
}
// 출처 : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/standard-library/input-stream-member-functions?view=msvc-170#vclrfthegetfunctionanchor12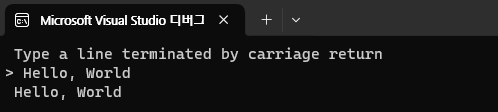
fflush
usage : fflush(stdin) or fflush(FILE *stream)
- 버퍼를 비움
- 스트림에 버퍼링된 데이터를 즉시 디스크에 쓰는 것을 의미합니다.
그래서 위아래로 파일 내용을 출력해서 테스트해보려했는데, 잘안됨 추후 추가
// crt_fflush.c
// Compile with: cl /W4 crt_fflush.c
// This sample gets a number from the user, then writes it to a file.
// It ensures the write isn't lost on crash by calling fflush.
#include <stdio.h>
int * crash_the_program = 0;
int main(void)
{
FILE * my_file;
errno_t err = fopen_s(&my_file, "myfile.txt", "w");
if (my_file && !err)
{
printf("Write a number: ");
int my_number = 0;
scanf_s("%d", &my_number);
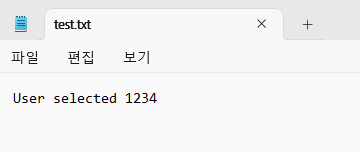
fprintf(my_file, "User selected %d\n", my_number);
// Write data to a file immediately instead of buffering.
fflush(my_file);
if (my_number == 5)
{
// Without using fflush, no data was written to the file
// prior to the crash, so the data is lost.
*crash_the_program = 5;
}
// Normally, fflush is not needed as closing the file will write the buffer.
// Note that files are automatically closed and flushed during normal termination.
fclose(my_file);
}
return 0;
}
// 출처 : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/c-runtime-library/reference/fflush?view=msvc-170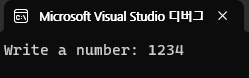
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
/*
* 작성일자 : 23.12.14
* 이슈사항 : scanf 실행 시 C6031: 반환 값이 무시되었습니다. 'scanf.' 에러 발생
* 해결방법 : pragma warning(disable:4996)을 추가
* 참고내용 : https://akdl911215.tistory.com/167
*/
using namespace std;
void ex1()
{
int a, b;
a = 5;
b = 7;
printf("a = %5d\nb = %5d\n", a, b);
printf("정수 2개 입력 : ");
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("a = %5d\nb = %5d\n", a, b);
}
void ex2() {
int a, b;
a = 7;
b = 9;
cout << "a = " << setw(5) << a << "\nb = " << setw(5) << b << endl;
cout << "정수 2개 입력 : ";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "a = " << setw(5) << a << "\nb = " << setw(5) << b << endl;
}
void ex3() {
char str[20] = "ABCD";
cout << str << endl;
fflush(stdin);
cout << "문자열 첫번째 입력: ";
// cin >> str;
// 공백 문자가 있을 경우 첫번째 argument만 불러옴
cin.get(str, 20);
cout << str << endl;
fflush(stdin);
// 키보드 버퍼를 지우지 않으면 엔터가 지워지지않아서 두번째 값을 입력받지 않음
cin.ignore();
/*
* 작성일자 : 23.12.14
* 이슈사항 : 강의내용과 다르게 fflush(stdin)을 해도 두번째 입력이 실행되지 않음
* 해결방법 : cin.ignore()을 추가
* 참고내용 : https://cboard.cprogramming.com/cplusplus-programming/76368-cin-get-twice-effect.html
*/
cout << "문자열 두번째 입력: ";
cin.get(str, 20);
cout << str << endl;
fflush(stdin);
}
void main() {
ex3();
}
'C++ > 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] 동적할당 (1) | 2023.12.18 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 래퍼런스(Reference) 변수, 포인터(Pointer) 변수 (0) | 2023.12.15 |
| [C++] bool 자료형 (0) | 2023.12.14 |
| [C++] 오버로딩, 디폴트 매개변수, 초기화 (0) | 2023.12.14 |
| [C++] namespace (0) | 2023.12.14 |



